Topic 1
Planet earth
Planet earth
Rocks and minerals
Rock: a solid mass of a mineral or a mixture of minterals
Mineral: a naturally occurring solid with a definite crystalline structure and chemical composition
Use of minerals
Rock salt --> cooking
Jade --> jewellery
Marble --> floor tiles
An ore is a mineral from which a constituent (usually a metal) can be profitable extracted
Common ores
Bauxite --> aluminium
Copper pyrite --> copper
Haematite --> iron
Extraction of metals from their ores
Process usually involved:
1. Mining of the ore
2. Concentrating the ore
3. Extraction of the metal from the concentrated one
4. Purification of the impure metal
1. Mining of the ore
2. Concentrating the ore
3. Extraction of the metal from the concentrated one
4. Purification of the impure metal
Haematite --> iron
iron(III) oxide + carbon --heat--> iron + carbon dioxide
Bauxite --> aluminium
aluminium oxide --electrolysis--> aluminium + oxygen
Silver
silver oxide --heat--> silver + oxygen
Limestone, chalk and marble
Limestone
Most common form of calcium carbonate
Use of Limestone
footpath
building statues
Crystalline form of calcium carbonate
Test for calcium carbonate in a sample of it
Calcium ions
calcium: brick-red flame
Carbonate ions
calcium carbonate + dilute HCL --> calcium chloride + carbon dioxide + water
turns limewater milky
Weathering and erosion of rocks
Weathering of rocks: slow process in which exposed rocks are broken down into smaller pieces
Physical weathering
by temperature changes
Chemical weathering
attack by acid
rainwater:
carbon dioxide + water --> carbonic acid
carbon dioxide + water --> carbonic acid
calcium carbonate + carbonic acid --> calcium hydrogencarbonate
calcium hydrogencarbonate: soluble in water --> limestone slowly worn away
formation of sinkholes areas
damage to limestone statues
attack by oxygen
Erosion of rocks: the slow process in which weathered rock pieces are transported away by gravity, wind and water
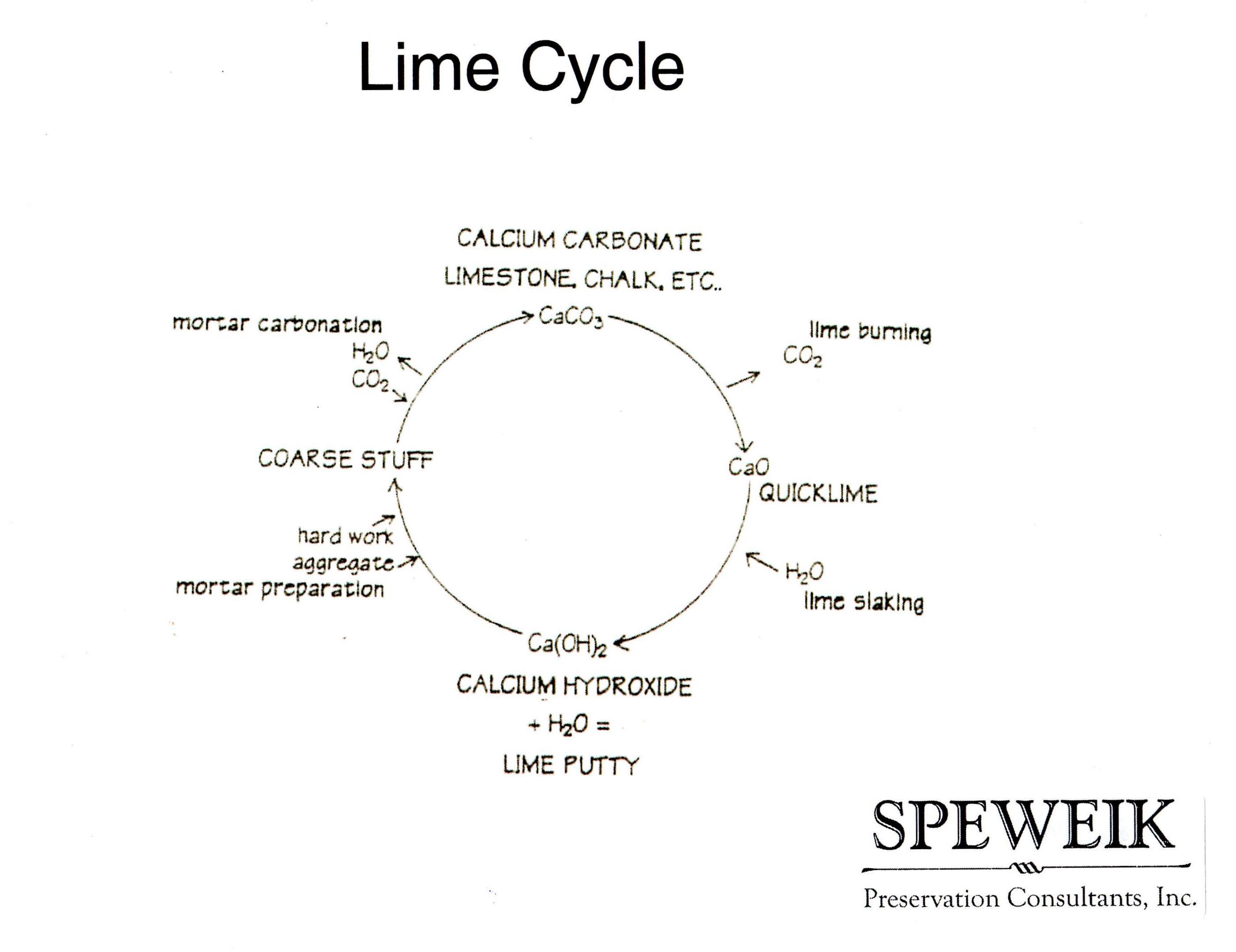
Chemical changes involving calcium carbonate
calcium carbonate --strong heat--> calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
quicklime treated with water:
calcium oxide + water --> calcium hydroxide (slaked lime)
calcium oxide + water --> calcium hydroxide (slaked lime)
white suspension is formed
filter the suspension --> solution: limewater
calcium hydroxide + carbon dioxide --> calcium carbonate + water
turns limewater milky
The atmosphere
The atmosphere is a gaseous layer surrounding the Earth
Air is a gaseous mixture making up the atmosphere
21% of oxygen
78%of nitrogen
1% of other gases
argon
use of argon
filling a light bulb
carbon dioxide
water vapour
Seperation of oxygen and nitrogen from air
nitrogen boils off first
Uses of nitrogen
provide an inert atmosphere
as a refrigerant
making ammonia
oxygen boils off last
Physical properties
slightly denser than air
slightly soluble in water
odourless
colourless
Test for oxygen
oxygen relights a glowing splint
Uses of oxygen
breathing
burning of fuels
Oceans
70% of earth is covered by water
seas
major components of salty sea water
68% sodium chloride
14.6% magnesium chloride
11,4% sodium sulphate
Extraction of common salt from sea water
evaporation
filtration
crystallization
Isolation of pure water from sea water
Test for sodium and chloride ions in common salt
sodium ions
flame test
chloride ions
silver nitrate test
Tests for the presence of water in a sample
by anhydrous copper(II) sulphate
by dry cobalt chloride paper
Electrolysis of sea water and uses of products
Uses of the products
Brine
Hygrogen
margarine, rocket fuel
Chlorine
water sanitation, bleach
Sodium hydroxide
aluminium extraction, soap