The Development of BC
The Oregon Territory
Between the Rockies and the Pacific ocean
Sparsely populated by the Europeans in 1819
Wanted by both the United States and Britain
The HBC had no interest in encouraging settlement, they preferred
to leave the region open for rich fur trade
to leave the region open for rich fur trade
The USA purchased territory westof Mississippi from France in 1803
This convinced most of the United States that they
were fated to control all of North America
were fated to control all of North America
This Idea was called
Manifest Destiny
Manifest Destiny
This Prompted aggressive settlement policy
in the Oregon Territory
in the Oregon Territory
US encouraged people from the eastern states to move here
Most Settled south of the Columbia River
By the 1830s, the population was growing rapidly
Important People
George Simpson, Manger of the HBC
Decided to build a new trading post in the
Oregon Territory
Oregon Territory
John McLoughlin, a French Canadian
Directed to expand the fur trade along the Pacific coast
to offset the dwindling fur stocks in the NorthWest
to offset the dwindling fur stocks in the NorthWest
capable and efficient administrator
The Colony of Vancouver Island
British Government created the crown colony of Vancouver Island
Important people
James Douglas, appointed governer
Chief Factor of Fort Victoria
Suggested that free land be offered to colonists
Convinced the British to put a naval base
near Fort Victoria
near Fort Victoria
The British Government
decided to charge for land at a rate
of $5 per acre
of $5 per acre
Minimum purchase of 20 acres
Grew Rapidly during the
1850's
1850's
Mines were developed near
Nanaimo and Cumberland
Nanaimo and Cumberland
Vancouver Island
The Cariboo Gold Rush
fueled by the gold rushes in North America,
South America, Australia, and New Zealand
South America, Australia, and New Zealand
Gold Rush
California
Gold was discovered in 1848
along the Sacramento River
along the Sacramento River
By mid-1850 The Gold had
been mined out
been mined out
Prospecting for gold was a very difficult task
The Fraser River
Governor Douglas was aware of the
social disruption caused by the
California Gold Rush
social disruption caused by the
California Gold Rush
Douglas feared that if another gold strike became known,
the colony of Vancouver Island might be invaded by thousands
of American miners
the colony of Vancouver Island might be invaded by thousands
of American miners
By the end of the summer of 1858 over 10 000
men worked claims along the Fraser Canyon,
mostly American
men worked claims along the Fraser Canyon,
mostly American
Douglas had no army or militia to call on
if serious trouble broke out
if serious trouble broke out
A pan of gold valued from 25 cents
to a dollar
to a dollar
Douglas' fears came true in 1857-1858
Prospectors of Washington and Oregon began moving
North to the banks of the Fraser and Thompson Rivers
North to the banks of the Fraser and Thompson Rivers
Word Reached San Francisco
450 unemployed miners arrived at Fort Victoria on April 25, 1858
Already living in the Fraser Canyon were the
Nlaka'pamux, Also called the Thompson River Salish
Nlaka'pamux, Also called the Thompson River Salish
Trouble began with an attack on a young
Nlaka'pamux
Nlaka'pamux
Several Gold miners were killed,
in Retaliation
in Retaliation
The discovery of the bodies started a panic
Informal militia's were quickly formed. made up of armed miners
Different leaders had different solutions
Some wanted a peaceful solution
Some advocated the complete destruction,
of the Nlaka'pamux
of the Nlaka'pamux
The Creation of British Columbia
The Smallpox Epidemic
In 1862, a San Francisco miner brought
small pox to Victoria
small pox to Victoria
The disease spread quick
Colonists were vaccinated
First Nations villages were quarantined
First Nations brought the smallpox with them
as they travelled north
as they travelled north
On Haida Gwaii over 70% of the population
died in the summer of 1862
died in the summer of 1862
Changes in Population
Non-First Nations- 774
First Nations- 30,000
Immigration
During the Cariboo and Fraser Gold Rushes, more
than 35,000 people arrived from alla over the world
to seek their fortunes
than 35,000 people arrived from alla over the world
to seek their fortunes
Gold was running out miners had to leave
Fewer people to pay taxes
By 1865, The Colony of Vancouver Island was in
$300,000 debt
$300,000 debt
The Colony of British Columbia owed more than
one million dollars
one million dollars
Only solution was to unite the two colonies
August 6,1866, the two colonies were officially untied
as the colony of British Columbia
as the colony of British Columbia
New node
The Confederation Debate
Arguments For and Against
Confederationists adopted resolutions that described how
and why British Columbia should join Canada
and why British Columbia should join Canada
Wanted the Dominion government to become responsible
for British Columbias debt\
for British Columbias debt\
Also wanted a wagon road to be built from Lake Superior
to New Westminister, providing a crucial trade link to the
rest of Canada
to New Westminister, providing a crucial trade link to the
rest of Canada
anti-confederationists wanted to maintain ties with Britain
and generally mistrusted Canadians
and generally mistrusted Canadians
Anothony Musgrave replaced Governor Seymour in late 1868
Musgraves instrustions were to get British Columbia to
join Confederation as wuick as possible
join Confederation as wuick as possible
With promise of a railway in 10 yrs
BC joined Canada, on July 20,1871
BC joined Canada, on July 20,1871
The New found Colony still needed more
people, more money and access to markets
people, more money and access to markets
Joining confederation would help solve those problems
Other Colonies had their doubts about confederation and
British Columbia was no exception
British Columbia was no exception
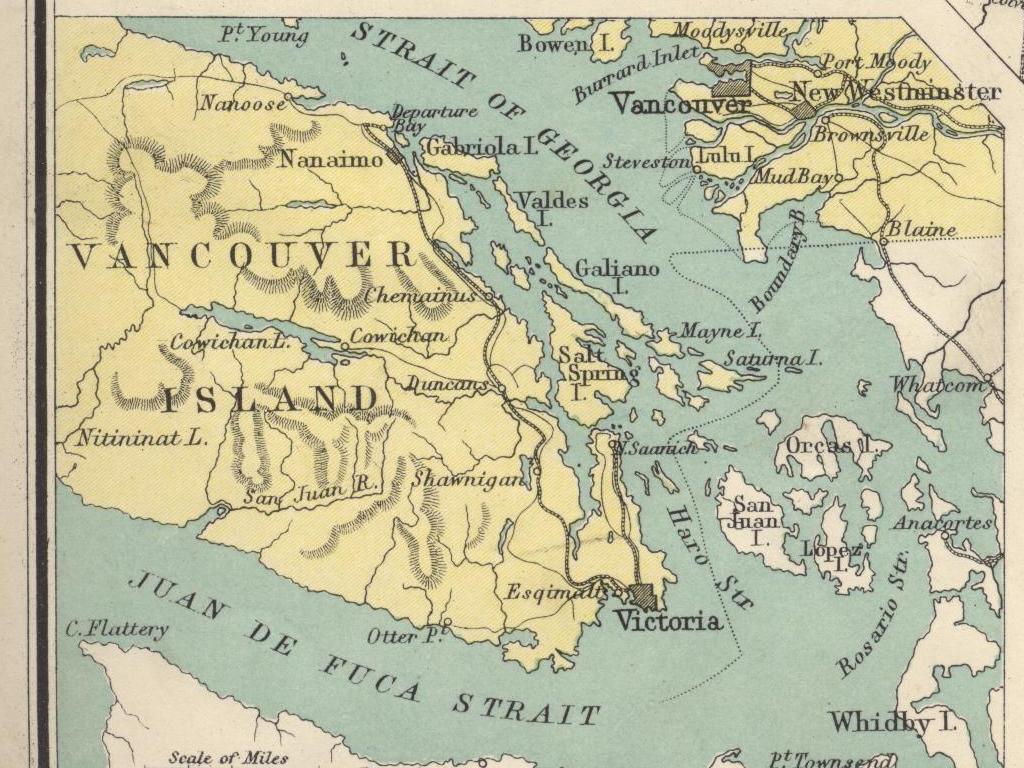
The Emergence of Vancouver
Industry Brings Development
Captain Edward stamp built Hastings Mill on the South
side of of the inlet
side of of the inlet
American entrepreneur Sewell Moody also
built a sawmill on the north side
built a sawmill on the north side
The mill and it's surrounding comunity
were known as Moodyville
were known as Moodyville
Both Mills specialized in logging "B.C. toothpicks"
They were prized as masts for sailing ships
and were exported around the world
and were exported around the world
Both Hastings Mill and Moodyville were officially dry until John "Gassy
Jack" Deighton appeared in Burrard Inlet in 1867, with a barrel of
Whiskey
Jack" Deighton appeared in Burrard Inlet in 1867, with a barrel of
Whiskey
Gassy's saloon became a popular place place
Soon other saloons and stores opened, and buildings were built along
shores of Burrard Inlet,
shores of Burrard Inlet,
Officially known as Granville, the village
was better known as Gastown, in honour of
Gassy Jack
was better known as Gastown, in honour of
Gassy Jack
The Railway arrives
1881 Port Moody was named the terminus, of
The Canadian Pacific Railway line
The Canadian Pacific Railway line
1884, William Van Horne Arrived to find the location of the CPR terminus
Finding what he was looking for, he named the site Vancouver announicing it would
be the CPR terminus
be the CPR terminus
CPR was completed and Vancouver was incorparated
by 1886
by 1886
B.C. was now in good contact with the rest of Canada
A Province of Diversity
The first non-European immigrants to British Columbia were the Kanakas
HBC were hiring Kanakas to work at posts
Black Immigrants
Black Immigratns made their way to north to Victoria
escaping slavery
escaping slavery
By the end of summer 1858 Hundreds of black Americans left "
for Vancouver Island
for Vancouver Island
formed a Militia
Jewish Immigrants
Many went into buisness selling to the goldminers on the mainland,
and Vancouver
and Vancouver
The Chinese
The largest group of non-European Immigrants
Started working abandoned claims by gold miners
Started opening stores
Discrimination was a big problem witht the Chinese and the Blacks