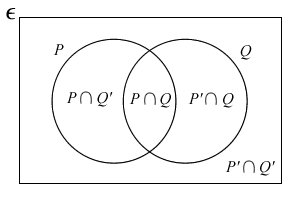Sets
Definition
Symbols
=
is equal to
∈
is an element of
∉
is not a element of
∋
contains as an element
{ }
curly brackets
used for containing elements
,
comma
used for separating elements
:
such that
used in set builder notation for dummy variable
. . .
many numbers
used for denote many or infinite numbers
'
complement
complement of a set includes all elements except elements from the mentioned set.
ε
universal set
set of all possible elements under consideration.
∅
empty set
set with no elements
⊆
subset
all elements in the aforementioned set is found in the following set and both may be equal sets
⊂
proper subset
all elements in the aforementioned set is found in the following set but both not equal sets
∩
intersection
set of elements that are found in both sets
∪
union
set of elements that are found in either of the sets or both sets
Modes of presentation
Listing the elements
A = { 1,2,3,4,5 }
Describing the elements
A = { positive integers less than 5 }
A is the set of positive integers less than 5
Set builder notation
A = { x : x = Z , 0 < x < 6 }
Subsets
Rules
an element can never be a subset
A = { 1 , 2 , 3 } , 1 ⊄ A , { 1 } ⊂ A
null set is a subset of any set
∅ ⊆ any set , { } ⊆ any set, but { ∅ } ⊈ any set
Subsets
no element in the aforementioned set is not found in the following set
Subset
⊆
both sets may be equal
to be used when the specific elements are not listed nor specified
tentative
if elements of both sets are specified, ⊆ is changed to ⊂ or =
If two sets are subsets of each other, they are equal sets
If A ⊆ B , B ⊆ A ⇒ A = B
Proper Subsets
⊂
both sets are specfied not equal
to be used when the specific elements are listed or specified
Supersets
⊇
A ⊆ B, then B ⊇ A.
⊃
C ⊂ D, then D ⊃ C
the set facing the curved side is usually the smaller set, unless both are equal sets.
Not a Subset / Superset
put a single diagonal up slash through it
⊈ ⊄ , ⊅ ⊉
Classification of numbers
Real Numbers ( ℝ )
Rational Number ( ℚ )
Integers ( Z )
Natural Number ( N ) or ( Z+ )
One ( 1 )
Prime number ( 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 . . . )
Composite number ( 4 , 6 , 8 , 9 . . . )
Zero ( 0 )
Negative Integer ( Z- )
Non - integer
Irrational number
Type of Sets
Null Set
A = ∅ = {}
{ ∅ } is not an emtpy set
Finite Set
A = { 4, 6, 10, 14}
Infinite Set
A = { ... -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 ... }
Universal Set
ε
Set of all possible elements under consideration.
Elements
" is a element of "
∈
" is not a element of "
∉
rules
only one element (not a set) can be "∈" of a set
A = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 } ⇒ 1 ∈ A, 2 ∈ A but { 1, 2 } ∉ A
s , S are considered different letters therefore different elements
a , { a } are different elements
Cardinal number
The number of elements in a set.
examples
If A = ∅ , n(A) = 0
If A = { 1, 4, 9, 16 } , n(A) = 4
If A = { 6, 7, 8, 9... }, n(A) = ∞
Equivalent sets
If n(A) = 7, n(B) = 7 ⇒ n(A) = n(B)
Complement
Complement of a set A
A'
Definition
A' = { x : x ∉ A , x ∈ ε }
Complement of a set includes all elements except elements from the mentioned set.
Venn Diagrams
Relationship of Sets
Disjoint Sets
A ∩ B = ∅ or A ⊆ B'
Intersecting Sets
A ∩ B ≠ ∅
Subset
A ⊆ B or B ⊇ A
Set Equality
A = B
Union of Sets
∪
The set of all elements which are either in A or B
A ∪ B = ( x : x ∈ A or x ∈ B )
Intersection of Sets
∩
The set of all elements which both in A and B
A ∩ B = ( x : x ∈ A and x ∈ B)
Set Equations
n( A ∪ B ) = n( A ) + n( B ) - n( A ∩ B )
n( P ∩ Q' ) + n( P ∩ Q ) + n( P' ∩ Q ) + n ( P' ∩ Q' ) = n( ε )
ε' = ∅
Done by
Reg No. 39 & 41 from Class 2 / 4